publications
Publications in reversed chronological order. If you need access to any manuscript, please don't hesitate to contact me.
- Collisionless and decentralized formation control for stringsYoung-Pil Choi, Dante Kalise, and Andrés A PetersNetworks and Heterogeneous Media, 2025
We address the design of decentralized feedback control laws inducing consensus and prescribed spatial patterns over a singular interacting particle system for string formations. The control design consists of a feedback term regulating the distance between each agent and pre-assigned subset of neighbours. Such a design represents an extension of existing control laws for 1d platoon formation control. For the proposed controller we study consensus emergence, collision-avoidance and formation control features in terms of energy estimates for the closed-loop system.
@article{choi2025collisionless, title = {Collisionless and decentralized formation control for strings}, author = {Choi, Young-Pil and Kalise, Dante and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A}, journal = {Networks and Heterogeneous Media}, volume = {20}, number = {3}, year = {2025}, publisher = {American Institute of Mathematical Sciences}, doi = {10.3934/nhm.2025036}, } -
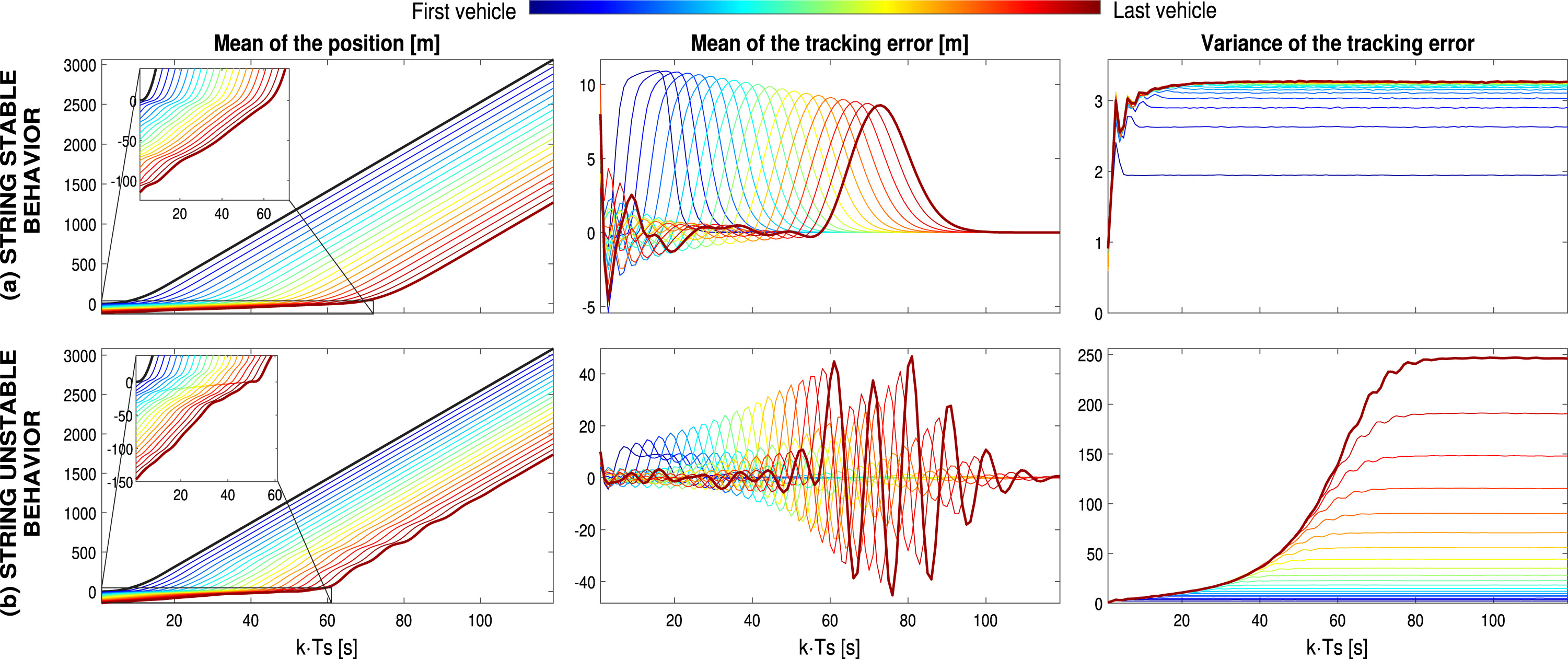 On stochastic string stability with applications to platooning over additive noise channelsFrancisco J Vargas, Marco A Gordon, Andrés A Peters, and 1 more authorAutomatica, 2025
On stochastic string stability with applications to platooning over additive noise channelsFrancisco J Vargas, Marco A Gordon, Andrés A Peters, and 1 more authorAutomatica, 2025This paper addresses the string stabilization of vehicular platooning when stochastic phenomena are inherent in inter-vehicle communication. To achieve this, we first provide two definitions to analytically assess the string stability in stochastic scenarios, considering the mean and variance of tracking errors as the platoon size grows. Subsequently, we analytically derive necessary and sufficient conditions to achieve this notion of string stability in predecessor-following linear platoons that communicate through additive white noise channels. We conclude that the condition ensuring string stability with ideal communication is essentially the same that achieves stochastic string stability when additive noise channels are in place and guarantees that the tracking error means and variances converge.
@article{vargas2025stochastic, title = {On stochastic string stability with applications to platooning over additive noise channels}, author = {Vargas, Francisco J and Gordon, Marco A and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Maass, Alejandro I}, journal = {Automatica}, volume = {171}, pages = {111923}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Pergamon}, doi = {10.1016/j.automatica.2024.111923}, } - Fundamental Limit on Time Headway for String Stability of Vehicular PlatooningMiaomiao Wang, Yamin Yan, Wuwei Wu, and 3 more authorsIFAC-PapersOnLine, 2025
In perhaps the simplest and most economical vehicle platoon control strategy, known as the predecessor-follower topology, time headway is the enabling and in fact the sole means to control inter-vehicle spacing by controlling vehicle speed relative to inter-vehicle distance. While it is desirable to maintain a small time headway to decrease road capacity usage, there is a limit to it in order to ensure the string stability of the platoon and hence secure vehicle safety; string stability is referred to as the property that disturbances are not amplified when propagating through the platoon. This paper provides an analytical expression of the fundamental lower bound to the time headway allowable to ensure string stability in the predecessor-follower platooning topology. The paper also analyzes the tracking performance of the vehicle system, presenting an explicit expression of the best achievable tracking error measured under an energy criterion.
@article{wang2025fundamental, title = {Fundamental Limit on Time Headway for String Stability of Vehicular Platooning}, author = {Wang, Miaomiao and Yan, Yamin and Wu, Wuwei and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Chen, Jie}, journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine}, volume = {59}, number = {13}, pages = {147--152}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2025.10.026}, } - Stochastic Lp string stability analysis in predecessor-following platoons under packet losses, arxiv=2403.11043Alejandro I Maass, Francisco J Vargas, Andres A Peters, and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2403.11043, 2024
@article{maass2024stochastic, title = {Stochastic Lp string stability analysis in predecessor-following platoons under packet losses, author = {Maass, Alejandro I and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andres A and Yuz, Juan I}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.11043}, year = {2024}, } - Experimental Sensitivity Analysis of a Control Algorithm for Line Following PlatooningFelipe Rifo, Nelson Salvador, Francisca Donoso, and 3 more authorsIn 2024 13th International Workshop on Robot Motion and Control (RoMoCo), 2024
In this paper, we consider a line-following platooning problem and analyze a cooperative strategy to address distance-sensing issues. The strategy relies on limiting the velocity of the followers, whenever their distance to the imme-diate predecessor is lost due to sensing restrictions or failure. Specifically, we conduct a set of experiments to evaluate the parameter sensitivity of the control algorithm, which corresponds to the percentage of the predecessor’s velocity that could be reached by each follower during a sensing loss scenario. We find that proper tuning must be carefully performed, as excessive velocity saturation may lead to undesired behaviors due to poor tracking capabilities, whereas insufficient saturation does not improve performance during unreliable sensing episodes. Our experiments are carried out on the RUPU platform, a low-cost scaled-down platform designed to study lateral and longitudinal control problems in path-following vehicle platooning.
@inproceedings{rifo2024experimental, title = {Experimental Sensitivity Analysis of a Control Algorithm for Line Following Platooning}, author = {Rifo, Felipe and Salvador, Nelson and Donoso, Francisca and Peters, Andr{\'e}s and Carvajal, Gonzalo and Vargas, Francisco}, booktitle = {2024 13th International Workshop on Robot Motion and Control (RoMoCo)}, pages = {43--48}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.1109/romoco60539.2024.10604358}, organization = {IEEE} } - Convergence analysis for platooning over coloured additive noise channelsFernando Sanhueza, Marco Gordon, Alejandro I Maass, and 2 more authorsIn 2024 European Control Conference (ECC), 2024
We consider a platooning control problem where the communication channels between vehicles are subject to coloured additive noises. Due to the stochastic nature of these channels, our analysis delves into examining the convergence of both the mean and variance of the vehicle tracking errors. We study the convergence as both time and number of vehicles grow unbounded. Our results include necessary and sufficient conditions for convergence and reveal that the colour of the noise does not impact the convergence characteristics of the error statistics, although it affects the values of the tracking error variances. Our findings offer insights into string stabilization. Numerical examples illustrate our results.
@inproceedings{sanhueza2024convergence, title = {Convergence analysis for platooning over coloured additive noise channels}, author = {Sanhueza, Fernando and Gordon, Marco and Maass, Alejandro I and Peters, Andr{\'e}s and Vargas, Francisco}, booktitle = {2024 European Control Conference (ECC)}, pages = {430--435}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.23919/ecc64448.2024.10591288}, organization = {IEEE} } - Exploring LQI Control in Sampled-Data Systems: A Numerical Study for First-Order SystemsLuis Severino, Fernando Sanhueza, Andrés Peters, and 1 more authorIn 2024 IEEE ANDESCON, 2024
This work aims to numerically study the impact of implementing a discrete-time Linear Quadratic Integral (LQI) controller. The discrete-time controller is based on a previously designed continuous-time one. The precision of this implementation is assessed by comparing the cost function of the continuous-time controller with the results obtained from implementing a discrete-time controller in a sampled-data feedback loop. Our analysis explores the effects of discretisation using various integral approximations and different sampling times. Our simulations show a disparity between continuous and sampled-data system costs for insufficiently low sampling periods, along with how the performance of the integration methods depends on the chosen weighting matrices. This research highlights the challenges and considerations in transitioning from continuous-time to discrete-time control.
@inproceedings{severino2024exploring, title = {Exploring LQI Control in Sampled-Data Systems: A Numerical Study for First-Order Systems}, author = {Severino, Luis and Sanhueza, Fernando and Peters, Andr{\'e}s and Vargas, Francisco}, booktitle = {2024 IEEE ANDESCON}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.1109/andescon61840.2024.10755529}, organization = {IEEE} } - RUPU: An Experimental Platform to Study Line-Following Platooning ProblemsCatalina Chaufleur, Carlos Escobar, Andrés Peters, and 2 more authorsIn 2023 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON), 2023
This paper presents RUPU, a low-cost scaled-down experimental platform for deployment and experimental testing of strategies to deal with the lateral and longitudinal control problems in path-following vehicle platooning. The platform represents a line-following platooning configuration with agents in a string formation following a line in the path, capturing the essence of the underlying control problems. This avoidsthe need for complex lane detection and path-planning algorithms, reducing the cost ofsensors and processing hardware. The platform provides agents equipped with sensing, actuating, and computing hardware to perform autonomous navigation over a flat surface.They also include wireless communication interfaces for cooperative platooning schemes,user interaction and remote monitoring. To illustrate the potential of RUPU, we perform a set of experiments and demonstrate its capability to perform repeatable and reproducible experiments for validating existing theoretical results and testing of new approaches for platooning control.
@inproceedings{chaufleur2023rupu, title = {RUPU: An Experimental Platform to Study Line-Following Platooning Problems}, author = {Chaufleur, Catalina and Escobar, Carlos and Peters, Andr{\'e}s and Carvajal, Gonzalo and Vargas, Francisco}, booktitle = {2023 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2023}, doi = {10.1109/chilecon60335.2023.10418641}, organization = {IEEE} } - A Cooperative Control Algorithm for Line and Predecessor Following Platoons Subject to Unreliable Distance MeasurementsCarlos Escobar, Francisco J Vargas, Andrés A Peters, and 1 more authorMathematics, 2023
This paper uses a line-following approach to study the longitudinal and lateral problems in vehicle platooning. Under this setup, we assume that inter-vehicle distance sensing is unreliable and propose a cooperative control strategy to render the platoon less vulnerable to these sensing difficulties. The proposed control scheme uses the velocity of the predecessor vehicle, communicated through a Vehicle-to-Vehicle technology, to avoid significant oscillations in the local speed provoked by tracking using unreliable local distance measurements. We implement the proposed control algorithm in the RUPU platform, a low-cost experimental platform with wireless communication interfaces that enable the implementation of cooperative control schemes for mobile agent platooning. The experiments show the effectiveness of the proposed cooperative control scheme in maintaining a suitable performance even when subject to temporal distortions in local measurements, which, in the considered experimental setup, arise from losing the line-of-sight of the local sensors in paths with closed curves.
@article{escobar2023cooperative, title = {A Cooperative Control Algorithm for Line and Predecessor Following Platoons Subject to Unreliable Distance Measurements}, author = {Escobar, Carlos and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Carvajal, Gonzalo}, journal = {Mathematics}, volume = {11}, number = {4}, pages = {801}, year = {2023}, publisher = {MDPI}, doi = {10.3390/math11040801}, } -
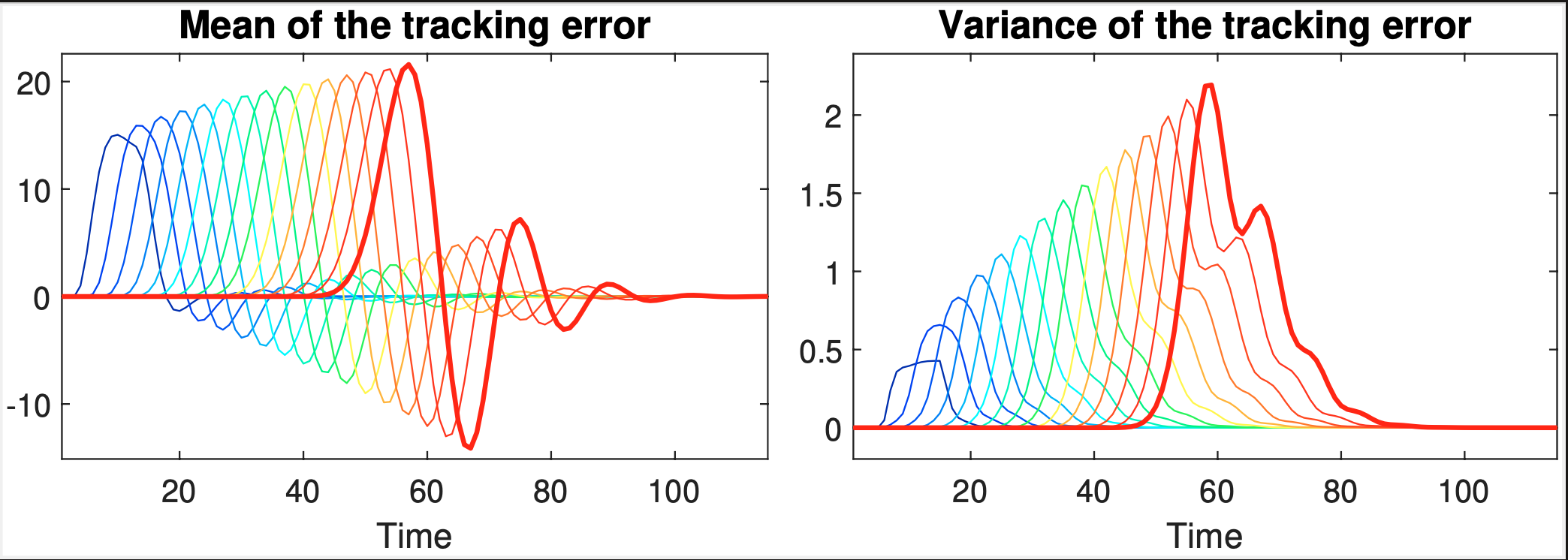 Mean square stability conditions for platoons with lossy inter-vehicle communication channelsMarco A Gordon, Francisco J Vargas, and Andrés A PetersAutomatica, 2023
Mean square stability conditions for platoons with lossy inter-vehicle communication channelsMarco A Gordon, Francisco J Vargas, and Andrés A PetersAutomatica, 2023This paper studies the mean-square stability of heterogeneous LTI vehicular platoons with inter-vehicle communication channels affected by random data loss. We consider a discrete-time platoon system with predecessor following topology and a constant time-headway spacing policy. Lossy channels are modeled by Bernoulli processes and allowed to be correlated in space. We make use of a class of compensation strategies to reduce the effect of data loss. Necessary and sufficient conditions are derived to guarantee the convergence of the mean and variance of the tracking errors, which depend not only on the controller design but also on the compensation strategy and the probabilities of successful transmission. We illustrate the theoretical results through numerical simulations, describing different platoon behaviors. We also provide insights on the mean-square stability as a necessary condition for string stability in this stochastic setting.
@article{gordon2023mean, title = {Mean square stability conditions for platoons with lossy inter-vehicle communication channels}, author = {Gordon, Marco A and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A}, journal = {Automatica}, volume = {147}, pages = {110710}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Pergamon}, doi = {10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110710}, } - Cooperative Identification of Multi-Agent Systems in Presence of Integral Action: Insights from a Two-Agent FrameworkCristóbal Huidobro, Francisco J Vargas, Andrés A Peters, and 1 more authorIFAC-PapersOnLine, 2023
This article addresses the parameter inference problem on dynamical systems in a cooperative setting. The dynamical systems contain integral action, which is of practical interest within cyber-physical systems. Given this dynamical characteristic of the problem, existing statistical results on system Identification are not straightforwardly applicable and hence adaptations are required. To this end, a formulation of the problem is presented and results highlighting the challenges of the given setup are discussed. Insights from a two-agent framework are used to formulate results and the next research steps on the topic, where the benefit of performing open-loop Identification on the variance of the parameter is highlighted and bias issues are discussed.
@article{huidobro2023cooperative, title = {Cooperative Identification of Multi-Agent Systems in Presence of Integral Action: Insights from a Two-Agent Framework}, author = {Huidobro, Crist{\'o}bal and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Valenzuela, Patricio E}, journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine}, volume = {56}, number = {2}, pages = {10216--10221}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2023.10.900}, } - Port Hamiltonian based model for platooning applications including air drag effectsFernando Sanhueza, Francisco Vargas, Hector Ramirez, and 1 more authorIFAC-PapersOnLine, 2023
This paper deals with platooning modeling considering the force provoked by the air drag in each vehicle. The proposed model is derived using a port-Hamiltonian approach in order to ensure the passivity of the whole system. The relation between the desired platooning formation and its implication on the air drag effect is highlighted. Simulation results illustrate the effect of air drag on the platoon behavior. The results of this work could serve as a basis for a platooning control scheme that explicitly includes the air drag force, as a function of the desired inter-vehicle distance, in the control loop.
@article{sanhueza2023port, title = {Port Hamiltonian based model for platooning applications including air drag effects}, author = {Sanhueza, Fernando and Vargas, Francisco and Ramirez, Hector and Peters, Andr{\'e}s}, journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine}, volume = {56}, number = {2}, pages = {3917--3922}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2023.10.1327}, } - LQI Control of a Self Balancing Robot: A Numerical Study of the Impact of the Integral ApproximationLuis Severino, Fernando Sanhueza, Andrés Peters, and 1 more authorIn 2023 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON), 2023
This work aims to explore the effects of the integral term in the discrete-time implementation of the LQI controller. To achieve this, a two-wheeled self-balancing robot system is used as a case study, and three types of numerical integration approximations are considered: Backward Euler, Forward Euler, and Tustin. Through simulations, the results obtained with each approximation are compared against the expected continuoustime design. The simulation results demonstrate that while there are no significant differences for small sampling times, the Tustin approximation exhibits notably better performance than the other alternatives as the sampling time increases.
@inproceedings{severino2023lqi, title = {LQI Control of a Self Balancing Robot: A Numerical Study of the Impact of the Integral Approximation}, author = {Severino, Luis and Sanhueza, Fernando and Peters, Andr{\'e}s and Vargas, Francisco}, booktitle = {2023 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2023}, doi = {10.1109/chilecon60335.2023.10418718}, organization = {IEEE} } - Exploring the Role of Sampling Time in String Stabilization for Platooning: An Experimental Case StudyFelipe I Villenas, Francisco J Vargas, and Andrés A PetersMathematics, 2023
In this article, we investigate the behavior of vehicle platoons operating in a predecessor-following configuration, implemented through sampled-data control systems. Our primary focus is to examine the potential influence of the sampling time on the string stability of the platoon. To address this, we begin by designing a string-stable platoon in continuous time. Subsequently, we consider the controller discretization process and proceed to simulate and implement the designed control strategy on an experimental platform at a scaled-down level. Through experimental testing and some theoretical results, we analyze the effects of different sampling times on the string stability performance of the platoon. We observe that an inappropriate selection of the sampling time can lead to a degradation in string stability within the platoon, making the choice of the sampling time crucial in maintaining the desired string stability properties. These findings highlight the importance of carefully considering the sampling time in the implementation of control systems for platooning applications.
@article{villenas2023exploring, title = {Exploring the Role of Sampling Time in String Stabilization for Platooning: An Experimental Case Study}, author = {Villenas, Felipe I and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A}, journal = {Mathematics}, volume = {11}, number = {13}, pages = {2923}, year = {2023}, publisher = {MDPI}, doi = {10.3390/math11132923}, } - A Kalman-based compensation strategy for platoons subject to data loss: Numerical and empirical studyFelipe I Villenas, Francisco J Vargas, and Andrés A PetersMathematics, 2023
This article considers a homogeneous platoon with vehicles that communicate through channels prone to data loss. The vehicles use a predecessor-following topology, where each vehicle sends relevant data to the next, and data loss is modeled through a Bernoulli process. To address the lossy communication, we propose a strategy to estimate the missing data based on the Kalman filter with intermittent observations combined with a linear extrapolation stage. This strategy enables the followers to better deal with data dropouts. We compare this approach to one purely based on the linear extrapolation of previous data. The performance of both strategies is analyzed through Monte Carlo simulations and experiments in an ad hoc testbed, considering various data loss and transmission loss probabilities depending on the inter-vehicle distance. The results show that for the considered cases, the proposed strategy outperforms the linear extrapolation approach in terms of tracking and estimation error variances. Our results also show that the proposed strategy can achieve string stability for the mean and variance for both the tracking and estimation errors in scenarios where the basic extrapolation strategy cannot.
@article{villenas2023kalman, title = {A Kalman-based compensation strategy for platoons subject to data loss: Numerical and empirical study}, author = {Villenas, Felipe I and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A}, journal = {Mathematics}, volume = {11}, number = {5}, pages = {1228}, year = {2023}, publisher = {MDPI}, doi = {10.3390/math11051228}, } - Experimental Validation of Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control Schemes Under the Presence of Time DelaysDiego Badillo, Felipe Villenas, Cristóbal Huidobro, and 2 more authorsIn 2022 IEEE International Conference on Automation/XXV Congress of the Chilean Association of Automatic Control (ICA-ACCA), 2022
This paper considers the experimental validation of theoretical results for cooperative platooning using the PL-TOON platform. In particular, we study an information relaying algorithm that enables a chain of autonomous vehicles, when there is perfect communication, to navigate in a string stable fashion, that is, without amplifying disturbances as they propagate along the vehicle string. Using the aforementioned experimental platform, we verify that such an algorithm can improve the string stability characteristics of a set of autonomous agents traveling in a tight formation on tracks. However, we also verify that the presence of time delays in the communication is very detrimental to the collective behavior of the agents, confirming theoretical results establishing this. We compare the experimental results with the theoretical ones and simulations of them, which highlights the capabilities of the experimental platform used. We also discuss alternatives for improving the robustness of similar cooperative platooning algorithms.
@inproceedings{badillo2022experimental, title = {Experimental Validation of Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control Schemes Under the Presence of Time Delays}, author = {Badillo, Diego and Villenas, Felipe and Huidobro, Crist{\'o}bal and Vargas, Francisco and Peters, Andr{\'e}s}, booktitle = {2022 IEEE International Conference on Automation/XXV Congress of the Chilean Association of Automatic Control (ICA-ACCA)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2022}, doi = {10.1109/ica-acca56767.2022.10005970}, organization = {IEEE} } - Nonlinear Time-Delay Observer-Based Control to Estimate Vehicle States: Lateral Vehicle ModelHicham El Aiss, Karina A Barbosa, and Andrés A PetersIEEE Access, 2022
This paper deals with the state estimation and control problem for nonlinear lateral vehicle dynamics with time delays. First, a novel time-varying delay vehicle model described as a Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy model is presented. In particular, it is considered that the lateral force contains an air resistance term which is assumed to be a quadratic function of the lateral vehicle velocity. A time-varying delay has been included in the vehicle states by a simple formula in order to capture brake actuation aspects or other practical aspects that may generate a delayed response, while the nonlinear part of the vehicle model is described as a Lipschitz function. A Takagi-Sugeno time-delay observer-based control that satisfies the Lipschitz condition is proposed to get closed-loop stability conditions. These results generalize existing ones in the literature on lateral dynamics control. Additionally, we provide a new methodology for the controller and observer gains design that can be cast as linear matrix inequality constraints. Finally, we illustrate our results with numerical examples, which also reveal the negative effect of not considering the presence of delays in the controller design.
@article{el2022nonlinear, title = {Nonlinear Time-Delay Observer-Based Control to Estimate Vehicle States: Lateral Vehicle Model}, author = {El Aiss, Hicham and Barbosa, Karina A and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A}, journal = {IEEE Access}, volume = {10}, pages = {110459--110472}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/access.2022.3210566}, } - Normalized-model reference system for parameter estimation of induction motorsAdolfo Véliz-Tejo, Juan Carlos Travieso-Torres, Andrés A Peters, and 2 more authorsEnergies, 2022
This manuscript proposes a short tuning march algorithm to estimate induction motors (IM) electrical and mechanical parameters. It has two main novel proposals. First, it starts by presenting a normalized-model reference adaptive system (N-MRAS) that extends a recently proposed normalized model reference adaptive controller for parameter estimation of higher-order nonlinear systems, adding filtering. Second, it proposes persistent exciting (PE) rules for the input amplitude. This N-MRAS normalizes the information vector and identification adaptive law gains for a more straightforward tuning method, avoiding trial and error. Later, two N-MRAS designs consider estimating IM electrical and mechanical parameters. Finally, the proposed algorithm considers starting with a V/f speed control strategy, applying a persistently exciting voltage and frequency, and applying the two designed N-MRAS. Test bench experiments validate the efficacy of the proposed algorithm for a 10 HP IM.
@article{veliz2022normalized, title = {Normalized-model reference system for parameter estimation of induction motors}, author = {V{\'e}liz-Tejo, Adolfo and Travieso-Torres, Juan Carlos and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Mora, Andr{\'e}s and Leiva-Silva, Felipe}, journal = {Energies}, volume = {15}, number = {13}, pages = {4542}, year = {2022}, publisher = {MDPI}, doi = {10.3390/en15134542}, } - A numerical study of a Kalman filtering based strategy for platooning with lossy communicationFelipe Villenas, Francisco Vargas, and Andrés PetersIn 2022 IEEE International Conference on Automation/XXV Congress of the Chilean Association of Automatic Control (ICA-ACCA), 2022
In this article, we consider homogeneous platoons where vehicles communicate through lossy links. We assume a predecessor following topology in where each vehicle sends its position to the immediate follower agent, and the transmission is subject to random data loss modeled as a Bernoulli process. A Kalman filtering based strategy is proposed to estimate the missing data. Such approach is compared with one where the missing data is replaced by a linear extrapolation based on previous data. The performance of each strategy is studied through numerical simulations for different data loss probabilities. The simulation results show that the Kalman filter-based strategy achieves a considerably better performance compared to the linear extrapolation case considering both, the tracking and the estimation errors.
@inproceedings{villenas2022numerical, title = {A numerical study of a Kalman filtering based strategy for platooning with lossy communication}, author = {Villenas, Felipe and Vargas, Francisco and Peters, Andr{\'e}s}, booktitle = {2022 IEEE International Conference on Automation/XXV Congress of the Chilean Association of Automatic Control (ICA-ACCA)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2022}, doi = {10.1109/ica-acca56767.2022.10006323}, organization = {IEEE} } - Sensor Calibration and Filtering for an Agent of the PL-TOON Platooning PlatformDiego Badillo, Cristóbal Huidobro, Felipe Villenas, and 2 more authorsIn 2021 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON), 2021
This paper reports techniques that improve the performance of the sensors of an experimental autonomous agent, which travels on tracks, part of the PL-TOON platform. These small agents of the platform can be used to build a platooning experimental setup, as they are able to track a follower, measure their own speed and communicate wirelessly with other agents of the platoon, enabling the implementation of cooperative formation control strategies for teaching and research. The improvements to the embedded software of the agents presented here focus on calibrating the sensors and identifying a dynamical model for the agents, filtering noise, and removing erroneous measurements that can appear under unfavorable environmental conditions for the sensors. The techniques were validated through experiments which we also report in this work.
@inproceedings{badillo2021sensor, title = {Sensor Calibration and Filtering for an Agent of the PL-TOON Platooning Platform}, author = {Badillo, Diego and Huidobro, Crist{\'o}bal and Villenas, Felipe and Peters, Andr{\'e}s and Vargas, Francisco}, booktitle = {2021 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2021}, doi = {10.1109/chilecon54041.2021.9702971}, organization = {IEEE} } - Comparison of Two Control Strategies for Platoons with Communication LossesMarco Gordon, Francisco Vargas, and Andrés PetersIn 2021 IEEE International Conference on Automation/XXIV Congress of the Chilean Association of Automatic Control (ICA-ACCA), 2021
This paper presents a comparison between two strategies to deal with data loss in a platoon of vehicles. We consider an homogeneous multi-agent LTI system comprised of vehicles using a predecessor follower topology and a constant time headway policy. Each agent in the string sends its current position to the immediate follower through a lossy channel modeled as a Bernoulli process. To maintain the speed of a vehicle in the event of communication loss, two control strategies are analyzed. When the data of the predecessor is not available, a first strategy uses the previously received data to estimate the lost position, while the other protocol uses the previously calculated control law. For both cases, we aim to analyze how the lossy channels affect the string stability and the overall behavior of the platoon. Through simulation results, we present the statistics of the position error and the tracking performance for different probabilities of losses and values of the time headway constant.
@inproceedings{gordon2021comparison, title = {Comparison of Two Control Strategies for Platoons with Communication Losses}, author = {Gordon, Marco and Vargas, Francisco and Peters, Andr{\'e}s}, booktitle = {2021 IEEE International Conference on Automation/XXIV Congress of the Chilean Association of Automatic Control (ICA-ACCA)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2021}, doi = {10.1109/icaacca51523.2021.9465306}, organization = {IEEE} } - Comparison of simple strategies for vehicular platooning with lossy communicationMarco A Gordon, Francisco J Vargas, and Andrés A PetersIEEE Access, 2021
This paper studies vehicle platooning with communication channels subject to random data loss. We focus on homogeneous discrete-time platoons in a predecessor-following topology with a constant time headway policy. We assume that each agent in the platoon sends its current position to the immediate follower through a lossy channel modeled as a Bernoulli process. To reduce the negative effects of data loss over the string stability and performance of the platoon, we use simple strategies that modify the measurement, error, and control signals of the feedback control loop, in each vehicle, when a dropout occurs. Such strategies are based on holding the previous value, dropping to zero, or replacing with a prediction based on a simple linear extrapolation. We performed a simulation-based comparison among a set of different strategies, and found that some strategies are favorable in terms of performance, while some others present improvements for string stabilization. These results strongly suggest that proper design of compensation schemes for the communications of interconnected multi-agent systems plays an important role in their performance and their scalability properties.
@article{gordon2021comparisoo, title = {Comparison of simple strategies for vehicular platooning with lossy communication}, author = {Gordon, Marco A and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A}, journal = {IEEE Access}, volume = {9}, pages = {103996--104010}, year = {2021}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/access.2021.3099404}, } - String Stability of a PI-controlled Vehicular PlatoonAntonia E Murillo, Francisco J Vargas, Andrés A Peters, and 1 more authorIn 2021 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON), 2021
This paper studies the asymptotic stability and string stability conditions for platoons composed of vehicles modelled by single integrator dynamics that are locally controlled by PI controllers with a constant time-headway spacing policy. The novelty of the work lies on not considering that the controller dynamics cancel the ones introduced by the spacing policy, which is a common strategy to simplify the analysis. In this setup, we obtain conditions for string stability that reveal two zones in the space spanned by the design parameters of the platoon that are compatible with this property. We also provide numerical simulations that verify the derived conditions.
@inproceedings{murillo2021string, title = {String Stability of a PI-controlled Vehicular Platoon}, author = {Murillo, Antonia E and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Rojas, Alejandro J}, booktitle = {2021 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2021}, doi = {10.1109/chilecon54041.2021.9703067}, organization = {IEEE} } - An Algebraic Formula for Performance Bounds of a Weighted H∞ Optimal Control ProblemAndrés A. Peters, Francisco J. Vargas, and Jie ChenIEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021
This article provides performance bounds for a particular
\mathcal H_∞ @article{peters2020algebraic, title = {An Algebraic Formula for Performance Bounds of a Weighted H∞ Optimal Control Problem}, author = {Peters, Andrés A. and Vargas, Francisco J. and Chen, Jie}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control}, volume = {66}, number = {2}, pages = {781-786}, year = {2021}, doi = {10.1109/TAC.2020.2982135}, keywords = {Eigenvalues and eigenfunctions;Optimal control;Sensitivity;Mathematical model;Optimized production technology;Poles and zeros;Discrete-time systems; $\mathcal {H}_\infty$ control;performance bounds} } -
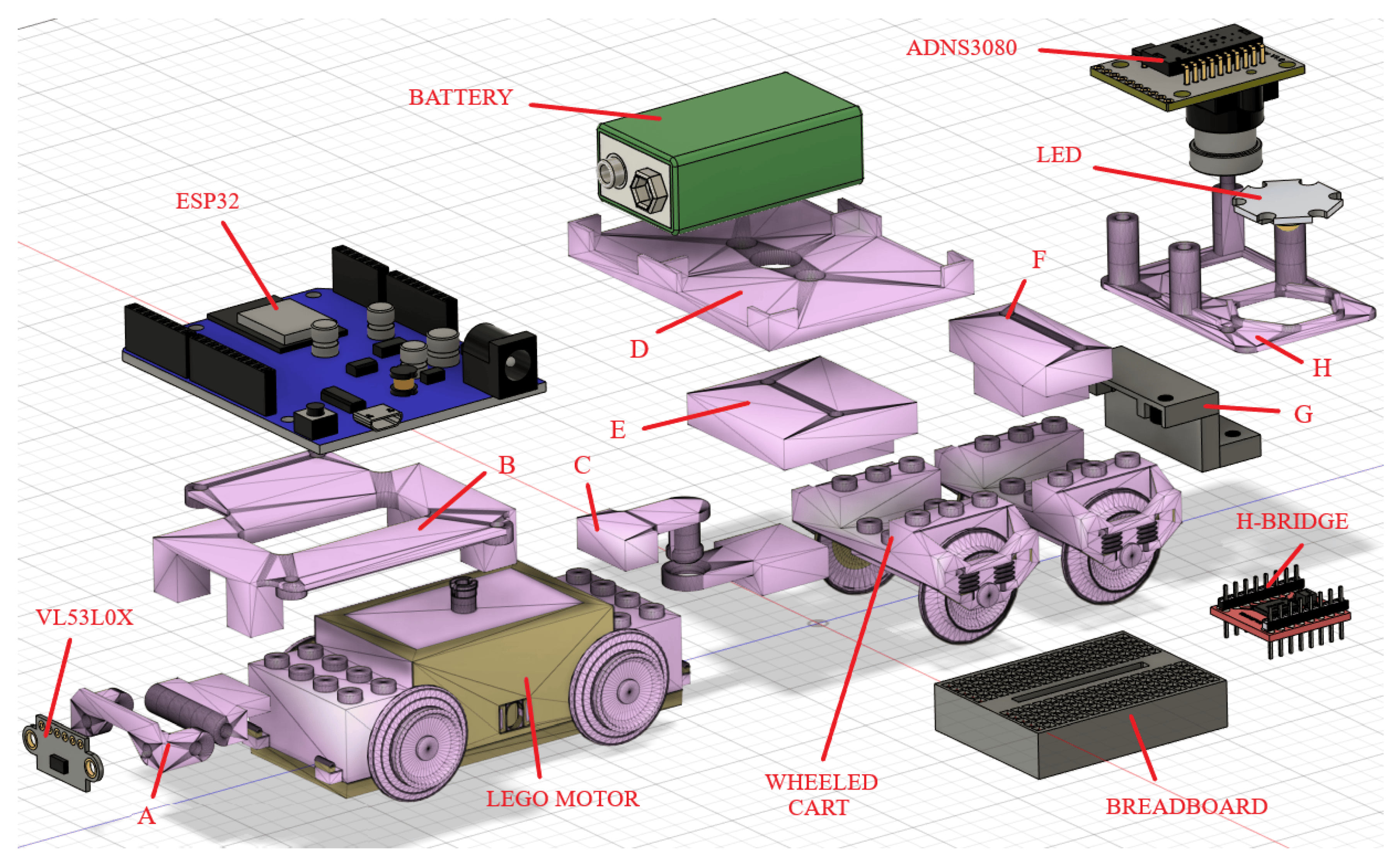 Pl-toon: A low-cost experimental platform for teaching and research on decentralized cooperative controlAndrés A Peters, Francisco J Vargas, Cristóbal Garrido, and 2 more authorsSensors, 2021
Pl-toon: A low-cost experimental platform for teaching and research on decentralized cooperative controlAndrés A Peters, Francisco J Vargas, Cristóbal Garrido, and 2 more authorsSensors, 2021In this paper, we present the development of a low-cost multi-agent system experimental platform for teaching, and research purposes. The platform consists of train-like autonomous agents equipped with local speed estimation, distance sensing to their nearest predecessor, and wireless communications with other agents and a central coordinator. The individual agents can be used for simple PID experiments in a classroom or laboratory setting, while a collection of agents are capable of performing decentralized platooning with cooperative adaptive cruise control in a variety of settings, the latter being the main goal of the platform. The agents are built from low cost components and programmed with open source software, enabling teaching experiences and experimental work with a larger number of agents that would otherwise be possible with other existing solutions. Additionally, we illustrate with experimental results some of the teaching activities that the platform is capable of performing.
@article{peters2021pl, title = {Pl-toon: A low-cost experimental platform for teaching and research on decentralized cooperative control}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Vargas, Francisco J and Garrido, Crist{\'o}bal and Andrade, Crist{\'o}bal and Villenas, Felipe}, journal = {Sensors}, volume = {21}, number = {6}, pages = {2072}, year = {2021}, publisher = {MDPI}, doi = {10.3390/s21062072}, } - Platoon stability conditions under inter-vehicle additive noisy communication channelsMarco A Gordon, Francisco J Vargas, Andrés A Peters, and 1 more authorIFAC-PapersOnLine, 2020
@article{gordon2020platoon, title = {Platoon stability conditions under inter-vehicle additive noisy communication channels}, author = {Gordon, Marco A and Vargas, Francisco J and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Maass, Alejandro I}, journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine}, volume = {53}, number = {2}, pages = {3150--3155}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.1057}, } - Constant Time-Headway Spacing Policy with Limited Communication Range for Discrete Time Platoon SystemsAndrés A Peters, and Alejandro J RojasIFAC-PapersOnLine, 2020
We present a study of the scaling properties of the interconnection of n agents (e.g. vehicles) through an r-lookahead network. These networks are considered as a possible implementation for vehicle platooning, although we do not make any assumptions on what the agents represent, and we assume them to be linear time invariant (LTI) discrete time systems, locally controlled by an LTI controller. In particular, we show that the r-lookahead topology gives rise to dynamics which can be studied from the roots of polynomials with transfer functions as their coefficients. Through numerical simulations, we study aspects relating the use of lookahead measurements and their effect on the value of a time headway constant needed for the scalability property known as string stability.
@article{peters2020constant, title = {Constant Time-Headway Spacing Policy with Limited Communication Range for Discrete Time Platoon Systems}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Rojas, Alejandro J}, journal = {IFAC-PapersOnLine}, volume = {53}, number = {2}, pages = {15198--15203}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.2298}, } - A low cost experimental platform for the study of scalability issues in multi-agent systemsCristóbal Andrade, Cristóbal Garrido, Andrés Peters, and 1 more authorIn 2019 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON), 2019
This paper describes the implementation of a low cost experimental testbed for the study of formation control of autonomous vehicles. The purpose of the platform is to serve as an aide for the teaching of control theory, embedded systems and networked multi-agent systems at a higher education level. Simultaneously, the platform has the capability to replicate recent theoretical results for 1 dimensional platooning of unmanned autonomous vehicles and it is flexible enough to motivate new lines of research in the same area. The platform consists of several model trains powered by a 9V DC motor. Each train is equipped with a low cost microcontroller unit (MCU) with WiFi capabilities, sensors, a battery and circuitry that allow its automation. All of the parts are mounted on a 3D printed chassis. Each MCU has access to the instantaneous velocity of its train, the distance to its immediate predecessor, and some measurements of other trains through the use of the Meassage Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) protocol. Using simple Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers and a highly decentralized networking scheme, the MCUs power the DC motors in order to reach a consensus velocity and a desired formation where the vehicles maintain fixed spacings, whenever possible. The wireless capabilities of the MCU allow for supervision of the agents, data acquisition and on the fly parameter configuration. The capabilities of the testbed are showcased through experimental results.
@inproceedings{andrade2019low, title = {A low cost experimental platform for the study of scalability issues in multi-agent systems}, author = {Andrade, Crist{\'o}bal and Garrido, Crist{\'o}bal and Peters, Andr{\'e}s and Vargas, Francisco}, booktitle = {2019 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2019}, doi = {10.1109/chilecon47746.2019.8988079}, organization = {IEEE} } -
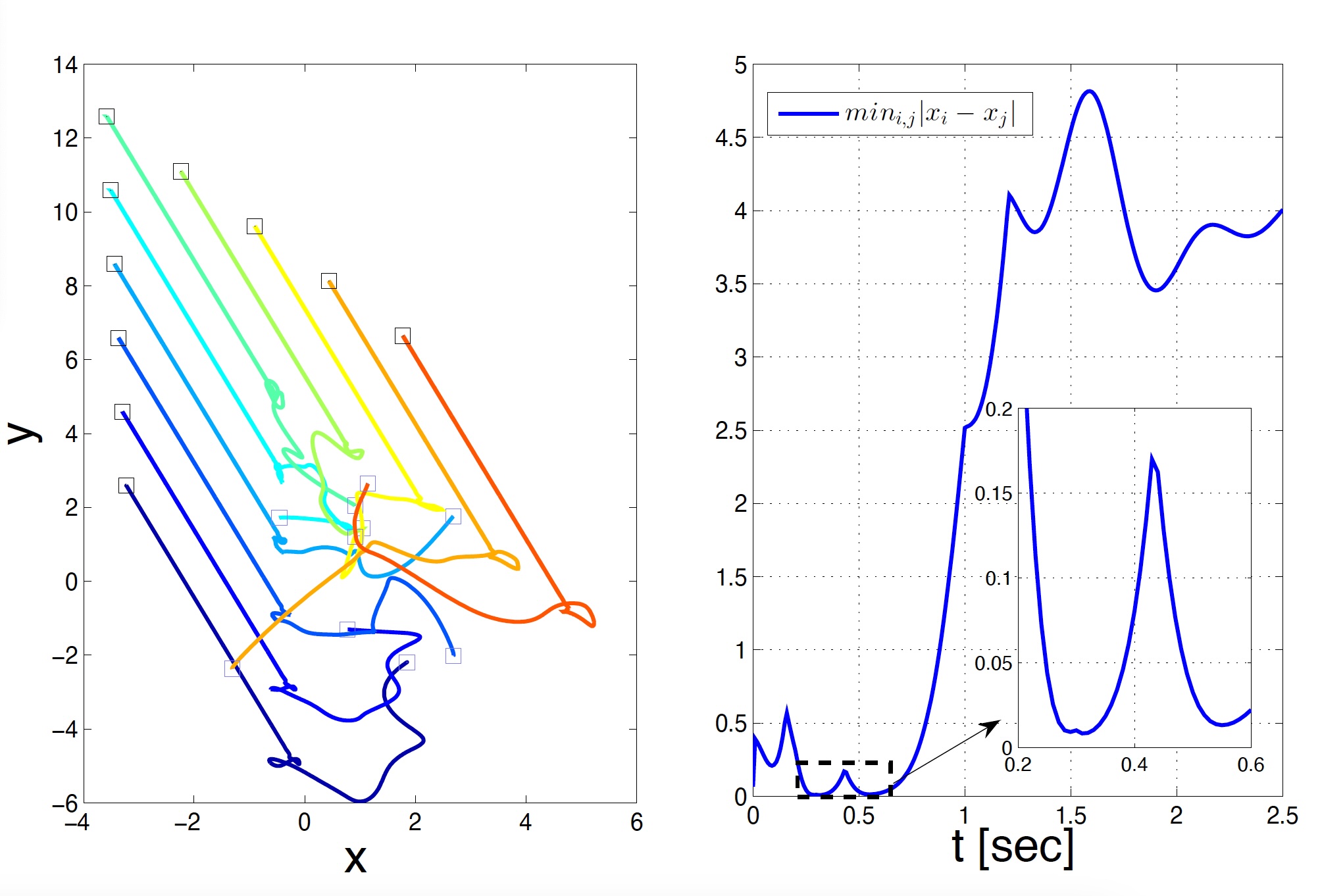 A collisionless singular Cucker–Smale model with decentralized formation controlYoung-Pil Choi, Dante Kalise, Jan Peszek, and 1 more authorSIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems, 2019
A collisionless singular Cucker–Smale model with decentralized formation controlYoung-Pil Choi, Dante Kalise, Jan Peszek, and 1 more authorSIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems, 2019We address the design of decentralized feedback control laws inducing consensus and prescribed spatial patterns over a singular interacting particle system of Cucker-Smale type. The control design consists of a feedback term regulating the distance between each agent and pre-assigned subset of neighbours. Such a design represents a multidimensional extension of existing control laws for 1d platoon formation control. For the proposed controller we study consensus emergence, collision-avoidance and formation control features in terms of energy estimates for the closed-loop system. Numerical experiments in 1, 2 and 3 dimensions assess the different features of the proposed design.
@article{choi2019collisionless, title = {A collisionless singular Cucker--Smale model with decentralized formation control}, author = {Choi, Young-Pil and Kalise, Dante and Peszek, Jan and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A}, journal = {SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems}, volume = {18}, number = {4}, pages = {1954--1981}, year = {2019}, publisher = {Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics}, doi = {10.1137/19M1241799}, dimensions = {}, } - Effects of speed saturation in a predecessor-following vehicle platoonAntonia Murillo, Francisco Vargas, and Andrés PetersIn 2019 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON), 2019
In this paper we perform a numerical study of the effect of speed saturation in a platoon of autonomous vehicles. In particular, the work is centered around studying the string stability of the platoon considering said speed limit. For this we will consider that each vehicle has the same dynamical description and that the desired inter-vehicle spacing depends on the speed of each agent. The analysis is done in discrete time and, besides the saturations, we assume that that the dynamics of the local control loops are linear time invariant. As a result, we illustrate numerically how the error due to said saturations may propagate along the string, losing the string stability property of the multi-agent system. We also illustrate that the undesireable effects of the saturation may be mitigated when a simple anti- windup scheme is incorporated to deal with them.
@inproceedings{murillo2019effects, title = {Effects of speed saturation in a predecessor-following vehicle platoon}, author = {Murillo, Antonia and Vargas, Francisco and Peters, Andr{\'e}s}, booktitle = {2019 IEEE CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON)}, pages = {1--7}, year = {2019}, doi = {10.1109/chilecon47746.2019.8988051}, organization = {IEEE} } - On the eigenvalues of a class of matrices with displacement structure arising in optimal controlAndrés A Peters, and Francisco J VargasarXiv preprint arXiv:1808.10730, 2018
@article{peters2018eigenvalues, title = {On the eigenvalues of a class of matrices with displacement structure arising in optimal control}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Vargas, Francisco J}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.10730}, year = {2018}, } - String stability for predecessor following platooning over lossy communication channelsFrancisco J Vargas, Alejandro I Maass, and Andrés A PetersIn Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, 2018
We study a platooning scheme where the commu-nication between agents is made through lossy channels. Each agent is modelled as a discrete-time LTI system controlled by a discrete-time LTI controller. The lossy channels are modelled using Bernoulli processes that represent random data dropouts. We consider a scheme that forces inter-vehicle spacings that increase with agents velocities. This is known as a constant time headway spacing policy, which has been shown to provide string stability for predecessor-following architectures. We analyse how the lossy channels impact the platoon string stability.
@inproceedings{vargas2018string, title = {String stability for predecessor following platooning over lossy communication channels}, author = {Vargas, Francisco J and Maass, Alejandro I and Peters, Andr{\'e}s A}, booktitle = {Hong Kong University of Science and Technology}, year = {2018}, } - Performance bounds of a SISO H∞ control problem with non-minimum phase plantsAndrés A Peters, and Francisco J VargasIn 2017 11th Asian Control Conference (ASCC), 2017
This work provides a methodology to study the performance bounds for a H∞ optimal control problem with discrete time LTI plants. In particular, we study a model matching problem with a stable scalar plant that possesses a single finite non-minimum phase zero and an arbitrary relative degree. The solution to this problem can be obtained by several methods that frequently lead to the use of numerical techniques. This usually hides the effect that the plant characteristics have in the optimal achievable value of the objective function. Alternatively, in this paper we use Nehari’s Theorem in order to obtain an eigenvalue problem that yields the optimal performance achievable with an one degree-of-freedom control loop. Given the structure of the control setup, we transform the eigenvalue problem into a non-linear equation, whose behaviour can be easily determined. The role that plant characteristics play in the achievable performance bound is made evident by this approach.
@inproceedings{peters2017performance, title = {Performance bounds of a SISO H∞ control problem with non-minimum phase plants}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Vargas, Francisco J}, booktitle = {2017 11th Asian Control Conference (ASCC)}, pages = {180--185}, year = {2017}, doi = {10.1109/ASCC.2017.8287163}, organization = {IEEE} } - String stability of a leader following formation control with dynamic weightsAndrés A PetersIn 2017 22nd International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR), 2017
In this work, we study the string stability properties of a leader following formation control architecture that uses non homogeneous weights for the leader and predecessor vehicle states. The architecture was presented recently [1] and it was shown to achieve constant inter-vehicle spacings (with no transient) for almost every vehicle pair when there are no disturbances at the followers. We expand the analysis of this interconnection by obtaining a condition on the design parameters that ensures the string stability of the interconnection to disturbances at any follower. Numerical simulations illustrate our results.
@inproceedings{peters2017string, title = {String stability of a leader following formation control with dynamic weights}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A}, booktitle = {2017 22nd International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR)}, pages = {290--294}, year = {2017}, doi = {10.1109/mmar.2017.8046841}, organization = {IEEE} } - Cyclic interconnection for formation control of 1-D vehicle stringsAndrés A Peters, Richard H Middleton, and Oliver MasonEuropean Journal of Control, 2016
In this paper, we study a formation control scheme for a 1-D string of vehicles. Each member tracks the movement of its immediate predecessor but also the first vehicle tracks the position of the last member of the string. We discuss conditions for the stability of the full interconnected system and show that if a constant spacing policy is used, the stability of the system is lost after the string size exceeds a certain number depending on the model parameters (vehicles and controllers). Additionally, we study the use of a constant time headway spacing policy. If the associated time headway parameter is greater than a critical value, the interconnected system is stable and string stable for any string size. Finally, we show that if an independent leader vehicle is added to the formation and every follower has access to this leader position, the cyclic formation with a constant spacing policy can be made stable and string stable by appropriately selecting a design parameter.
@article{peters2016cyclic, title = {Cyclic interconnection for formation control of 1-D vehicle strings}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Middleton, Richard H and Mason, Oliver}, journal = {European Journal of Control}, volume = {27}, pages = {36--44}, year = {2016}, publisher = {Elsevier}, doi = {10.1016/j.ejcon.2015.12.002}, } - Leader following with non-homogeneous weights for control of vehicle formationsAndrés A Peters, Oliver Mason, and Richard H MiddletonIn 2016 IEEE Conference on Control Applications (CCA), 2016
In this paper, we study a formation control scheme that achieves a tight formation in a 1D platoon. The scheme achieves constant inter-vehicle spacings (with no transient) for almost every vehicle pair whenever there are no disturbances. We build up from the basic leader following approach with a modification in the weight selection. In particular, each member tracks the movement of its immediate predecessor but also uses the leader state, which needs to be transmitted, in order to achieve a tight formation. The key design choice is the use of filters for the measurements that set the transfer functions from the leader trajectory to the inter-vehicle spacings to zero whenever possible. We support the analysis of the architecture with numerical simulations.
@inproceedings{peters2016leader, title = {Leader following with non-homogeneous weights for control of vehicle formations}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Mason, Oliver and Middleton, Richard H}, booktitle = {2016 IEEE Conference on Control Applications (CCA)}, pages = {109--113}, year = {2016}, doi = {10.1109/cca.2016.7587830}, organization = {IEEE} } - Cyclic interconnection in 1-D vehicle formation controlAndrés A Peters, Oliver Mason, and Richard H MiddletonIn 2014 European Control Conference (ECC), 2014
In this paper, we study a formation control scheme for a 1D string of vehicles. Each member tracks the movement of its immediate predecessor but also the first vehicle tracks the position of the last member of the string. We discuss conditions for the stability of the full interconnected system and show that if a constant inter-vehicle spacing policy is used, the interconnection becomes unstable after the string size surpasses a critical value. Moreover, we show that if constant time headway is used in the spacing policy, stability can be recovered for any string size. String stability is also achieved as a consequence.
@inproceedings{peters2014cyclic, title = {Cyclic interconnection in 1-D vehicle formation control}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Mason, Oliver and Middleton, Richard H}, booktitle = {2014 European Control Conference (ECC)}, pages = {1548--1553}, year = {2014}, doi = {10.1109/ecc.2014.6862586}, organization = {IEEE} } -
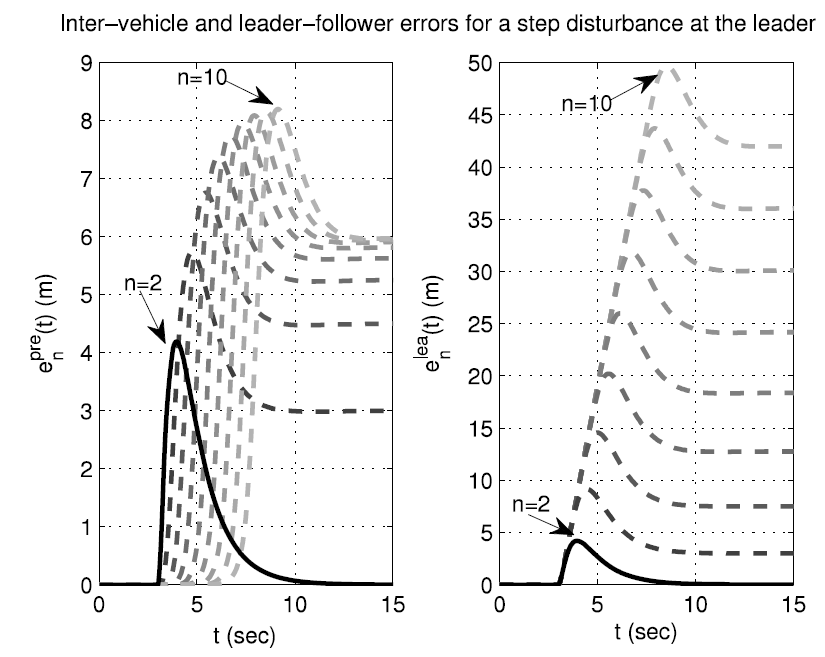 Leader tracking in homogeneous vehicle platoons with broadcast delaysAndrés A Peters, Richard H Middleton, and Oliver MasonAutomatica, 2014
Leader tracking in homogeneous vehicle platoons with broadcast delaysAndrés A Peters, Richard H Middleton, and Oliver MasonAutomatica, 2014For vehicle platoons, the leader following control architecture is known to be capable of achieving string stability while maintaining tight formations. In this paper, we study a variety of schemes where the leader state is available to the other members of the platoon. We show that in some cases it is possible to achieve string stability in the presence of certain amounts of time delay in the leader state reception. We also compare other properties of the different schemes and discuss some of their advantages and disadvantages.
@article{peters2014leader, title = {Leader tracking in homogeneous vehicle platoons with broadcast delays}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Middleton, Richard H and Mason, Oliver}, journal = {Automatica}, volume = {50}, number = {1}, pages = {64--74}, year = {2014}, publisher = {Pergamon}, doi = {10.1016/j.automatica.2013.09.034}, } - On the error estimates for the finite element approximation of a class of boundary optimal control systemsPablo Gamallo, Erwin Hernández, and Andres PetersNumerical functional analysis and optimization, 2011
In this article, we consider an application of the abstract error estimate for a class of optimal control systems described by a linear partial differential equation (as stated in Numer. Funct. Anal. Optim. 2009; 30:523–547). The control is applied at the boundary and we consider both, Neumann and Dirichlet optimal control problems. Finite element methods are proposed to approximate the optimal control considering an approximation of the variational inequality resulting from the optimality conditions; this approach is known as classical one. We obtain optimal order error estimates for the control variable and numerical examples, taken from the literature, are included to illustrate the results.
@article{gamallo2011error, title = {On the error estimates for the finite element approximation of a class of boundary optimal control systems}, author = {Gamallo, Pablo and Hern{\'a}ndez, Erwin and Peters, Andres}, journal = {Numerical functional analysis and optimization}, volume = {32}, number = {4}, pages = {383--396}, year = {2011}, publisher = {Taylor \& Francis Group}, doi = {10.1080/01630563.2010.542359}, } - Leader velocity tracking and string stability in homogeneous vehicle formations with a constant spacing policyAndrés A Peters, and Richard H MiddletonIn 2011 9th IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA), 2011
For vehicle platoons, the leader following control structure is well known for being capable of achieving string stability. In this paper, the linear string case is modified so that each follower tracks the instantaneous velocity of the leader in addition to the position of its predecessor. We show that it is possible to achieve string stability, under some basic assumptions, with this approach. We also discuss some of the benefits of the use of this method such as lowered coordination requirements and simplified communication needs.
@inproceedings{peters2011leader, title = {Leader velocity tracking and string stability in homogeneous vehicle formations with a constant spacing policy}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Middleton, Richard H}, booktitle = {2011 9th IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA)}, pages = {42--46}, year = {2011}, doi = {10.1109/icca.2011.6138068}, organization = {IEEE} } - An analytic characterization of a stabilizing feedback for LTI plantsAndrés A Peters, Diego A Oyarzún, Eduardo I Silva, and 1 more authorIn 2009 European Control Conference (ECC), 2009
The characterization of all stabilizing controllers via the Youla Parameterization requires prior knowledge of one stabilizing feedback. This task is trivial in the case of stable plants. In the unstable case, one needs to use a suitable design technique to obtain such a stabilizing controller. The resulting controller is usually not an explicit function of plant dynamical features. In this paper, we propose a stabilizing controller design such that the sensitivity function can be expressed as an explicit function of the non-minimum phase zeros, time delays, and unstable poles of the plant (and their directions in the multiple-input multiple-output case). These dynamical features are known to impose fundamental limitations on control performance. The results in this paper highlight their relevance since they are shown to be the minimum information required to build a stabilizing controller.
@inproceedings{peters2009analytic, title = {An analytic characterization of a stabilizing feedback for LTI plants}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Oyarz{\'u}n, Diego A and Silva, Eduardo I and Salgado, Mario E}, booktitle = {2009 European Control Conference (ECC)}, pages = {231--235}, year = {2009}, doi = {10.23919/ecc.2009.7074409}, organization = {IEEE} } - Performance Bounds in H∞ Optimal Control for Stable SISO Plants With Arbitrary Relative DegreeAndrés A Peters, and Mario E SalgadoAutomatic Control, IEEE Transactions on, 2009
This note deals with performance bounds for the H infin-optimal control of discrete-time LTI plants. The case studied corresponds to stable scalar plants with arbitrary relative degree but no finite non-minimum phase zero. By using Nehari’s Theorem and a reformulation of the standard Youla Parameterization a closed-form expression for the characteristic polynomial of the associated eigenvalue problem is obtained. Also, we derive an analytic expression for the optimal H infin cost as a function of the plant relative degree.
@article{peters2009performance, title = {Performance Bounds in H∞ Optimal Control for Stable SISO Plants With Arbitrary Relative Degree}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Salgado, Mario E}, journal = {Automatic Control, IEEE Transactions on}, volume = {54}, number = {8}, pages = {1987--1990}, year = {2009}, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/TAC.2009.2023966}, } - Performance bounds in linear control of unstable MIMO systems with pole location constraintAndrés A Peters, Mario E Salgado, and Eduardo I SilvaSystems & Control Letters, 2008
This paper proposes a methodology to compute quadratic performance bounds when the closed loop poles of a discrete-time multivariable control loop are confined to a disk, centred at the origin, and with radius less than one. The underlying philosophy in this constraint is to avoid certain undesirable dynamic features which arise in quadratic optimal designs. An expression for the performance loss due to the pole location constraint is also provided. Using numerical examples, we show that the performance loss is compensated by an improved transient performance, specially visible in the control signals.
@article{peters2008performance, title = {Performance bounds in linear control of unstable MIMO systems with pole location constraint}, author = {Peters, Andr{\'e}s A and Salgado, Mario E and Silva, Eduardo I}, journal = {Systems \& Control Letters}, volume = {57}, number = {5}, pages = {392--399}, year = {2008}, publisher = {North-Holland}, doi = {10.1016/j.sysconle.2007.10.003}, } - Performance bounds in MIMO linear control with pole location constraintAA Peters, ME Salgado, and EI Silva-VeraIn 2007 Mediterranean Conference on Control & Automation, 2007
In this paper, achievable performance bounds in the linear control of stable MIMO linear discrete time systems are derived. The cost function to be minimized is the 2 - norm of the tracking error for a vector step reference, under the constraint that the closed loop poles lie in a prescribed region. The computation of the performance limitation requires the factorization of the plant model using interactors, which capture the finite and infinite non-minimum phase zeros, and their associated directions. The controller achieving the optimal bound is also computed.
@inproceedings{peters2007performance, title = {Performance bounds in MIMO linear control with pole location constraint}, author = {Peters, AA and Salgado, ME and Silva-Vera, EI}, booktitle = {2007 Mediterranean Conference on Control \& Automation}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2007}, doi = {10.1109/med.2007.4433877}, organization = {IEEE} }
